 |
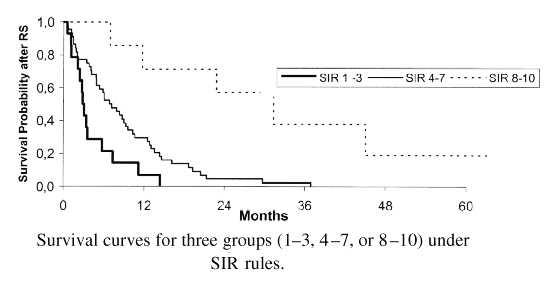
Survival by SIR Group: SIR 1-3: 2.9 months SIR 4-7: 7.0 months SIR 8-10: 31.4 months |
Radiosurgery for brain metastases: a score index for predicting prognosis.Weltman E,Department of Radiation Oncology, Sao Paulo, Brazil PURPOSE: To analyze a prognostic score index for patients with brain metastases submitted to stereotactic radiosurgery (the Score Index for Radiosurgery in Brain Metastases [SIR]). Actuarial survival of 65 brain metastases patients treated with radiosurgery between July 1993 and December 1997 was retrospectively analyzed. Prognostic factors included age, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), extracranial disease status, number of brain lesions, largest brain lesion volume, lesions site, and receiving or not whole brain irradiation. The SIR was obtained through summation of the previously noted first five prognostic factors. Median overall survival from radiosurgery was 6.8 months. Utilizing univariate analysis, extracranial disease status, KPS, number of brain lesions, largest brain lesion volume, RPA, and SIR were significantly correlated with prognosis. Median survival for the RPA classes 1, 2, and 3 was 20.19 months, 7.75 months, and 3. 38 months respectively (p = 0.0131). Median survival for patients, grouped under SIR from 1 to 3, 4 to 7, and 8 to 10, was 2.91 months, 7.00 months, and 31.38 months respectively (p = 0.0001). |
| Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 | |
| Age in years | 60 or older | 51 - 59 | under 50 |
| Karnofsky | 50 or less | 60 - 70 | over 70 |
| Systemic disease | progressive | stable or partial remis. | CR or NED |
| largest lesion volume | over 13cc | 5 - 13cc | under 5cc |
| number brain lesions | 3 or more | 2 | 1 |
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000 Mar 15;46(5):1155-61
 |
Survival by SIR Group: SIR 1-3: 2.9 months SIR 4-7: 7.0 months SIR 8-10: 31.4 months |
|
![]()
![]()