|
|
Start with
what
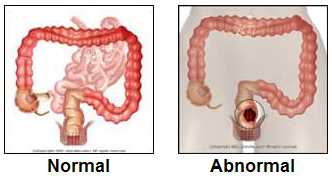
is colon or rectal cancer? Then
read the NCI booklet,
and the Cancer Net Patient sites for
colon and
rectum,
and a review about the cause of colon and rectal cancer
here and good patient
information from up-to-date
here and the other good colon and rectal cancer links.
Diet and cancer
here.
And see what are the most common locations for cancer
and here.
Age and colon and rectal cancer.
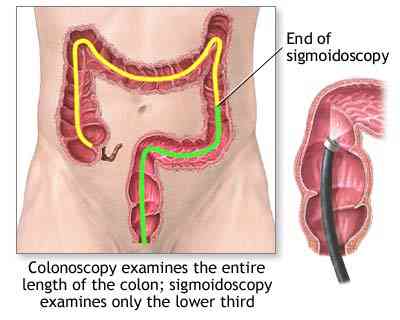
Go here for a review on symptoms
and evaluation.
Main colon and rectal anatomy section go here, and for pictures of CT or PET
Scans go here
See the screening or prevention (here and here) or the section about genetics or hereditary colon cancer