| Subgroup Analyses of the 2 Recursive
Partitioning Analysis Classes for Survival,
Entire Brain Control, Local Control, and
Brain Control Distant From Treated
Metastases: Potential Impact of the
Treatment Schedule |
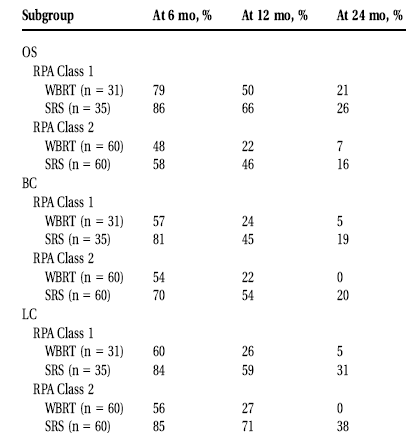 |
OS indicates overall
survival; RPA, recursive partitioning
analysis; WBRT, whole-brain radiotherapy;
SRS, stereotactic radiosurgery; BC, brain
control (entire brain control); LC, local
control; DC, distant control (brain control
from treated metastasis).
|
|
RESULTS.
On multivariate analysis
of OS, age ( risk ratio [RR], 1.51; P = .024), Karnofsky
performance status (KPS) (RR, 1.98; P = .002), and
extracranial metastases (RR, 2.26; P < .001) were
significant, whereas the radiation regimen was not
significant (P = .89). On multivariate analysis of BC,
only the radiation regimen (RR, 1.33; P = .003) was
found to be significant. On multivariate analysis of LC,
radiation regimen (RR, 1.63; P < .001) and sex (RR,
1.62; P = .022) were significant. On multivariate
analysis of DC, KPS (RR, 1.85; P = .049) and
extracranial metastases (RR, 1.69; P = .047) were
significant. The radiation regimen was not found to be
significant even on univariate analysis (P = .80). In
RPA class subgroup analyses, BC and LC were better after
SRS than WBRT for patients in RPA Classes 1 and 2,
whereas OS and DC did not differ significantly.
CONCLUSIONS.
For patients in RPA
Classes 1 and 2 who had 1 to 3 brain metastases,
SRS alone was associated with improved BC and LC
compared with 30 to 40 Gy WBRT, whereas OS and DC were
not significantly different. Similar results were
observed in separate subgroup analyses of patients in
RPA Class 1 and RPA Class 2. Cancer 2007. © 2007
American Cancer Society. |